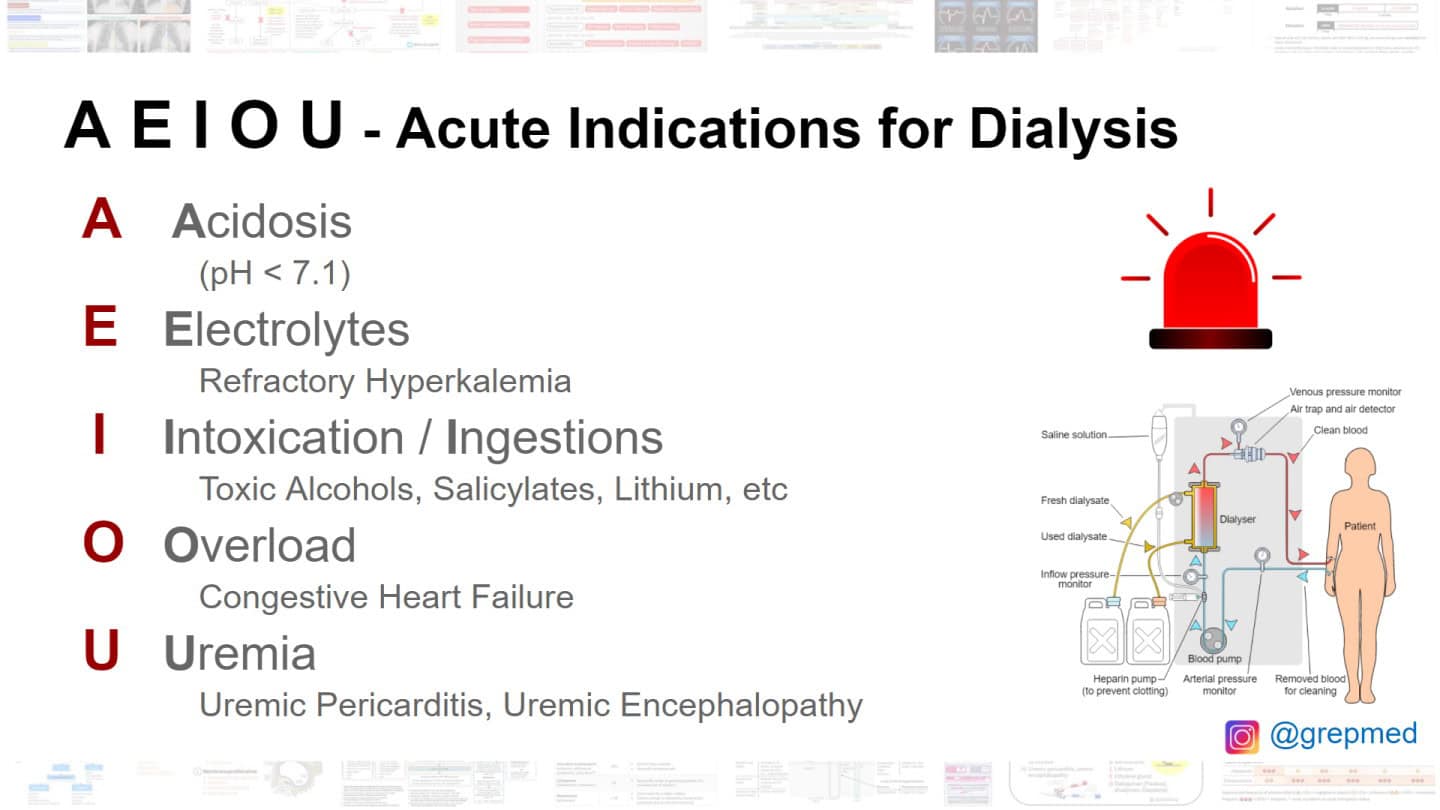
Indications for dialysis in Acute Kidney Injury(AKI) pt.
A – Acidosis – metabolic acidosis with a pH <7.1
E – Electrolytes – refractory hyperkalemia with a serum potassium >6.5 mEq/L or rapidly rising potassium levels; see this post for a review of the causes and management of hyperkalemia
I – Intoxications – use the mnemonic SLIME to remember the drugs and toxins that can be removed with dialysis: salicylates, lithium, isopropanol, methanol, ethylene glycol
O – Overload – volume overload refractory to diuresis
U – Uremia – elevated BUN with signs or symptoms of uremia, including pericarditis, neuropathy, uremic bleeding, or an otherwise unexplained decline in mental status (uremic encephalopathy)